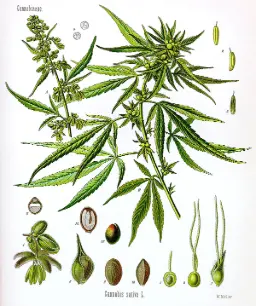
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a plant in the botanical class of Cannabis sativa cultivars grown specifically for industrial and consumable use. It can be used to make a wide range of products.[1] Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants on Earth.[2] It was also one of the first plants to be spun into usable fiber 50,000 years ago.[3] It can be refined into a variety of commercial items, including, paper, rope, textiles, clothing, bioplastics, paint, insulation, biofuel, and food.
[4][5]
Uses
There are over 50,000+ uses for industrial hemp:
Agriculture Manufacturing Construction Energy Transportation Food Environment Technology Economics Entertainment Research Healthcare & Fitness Hospitality Future Communications Mass Media Land Management Cooperative Entity Conversion Legal Professions Careers Jobs and Working Employment Definitions Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's)
Biology
Learn about Hemp: Taxonomy, Known Relatives, Cannabinoid containing plants, Kranz Anatomy, C4 Carbon Fixation
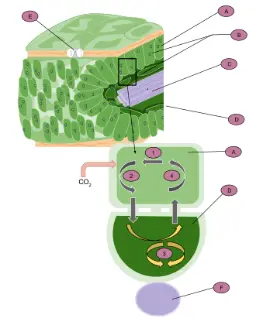
C4 carbon fixation or the Hatch–Slack pathway is one of three known photosynthetic processes of carbon fixation in plants. It owes the names to the 1960s discovery by Marshall Davidson Hatch and Charles Roger Slack.[1]
C4 fixation is an addition to the ancestral and more common C3 carbon fixation. The main carboxylating enzyme in C3 photosynthesis is called RuBisCO, which catalyses two distinct reactions using either CO2 (carboxylation) or oxygen (oxygenation) as a substrate. RuBisCO oxygenation gives rise to phosphoglycolate, which is toxic and requires the expenditure of energy to recycle through photorespiration. C4 photosynthesis reduces photorespiration by concentrating CO2 around RuBisCO.
History
Hemp is one of the oldest plants humans have grown and used. Hemp was domesticated in Asia over 10,000 years ago. It was already used to make clothes, ropes, and an early form of paper. The seeds were eaten, and the plant had medicinal uses. From there the use of hemp spread. In Europe, hemp was at least used 5,500 years ago. It is one of the earliest domesticated plants recorded.[1] It is quite strong and does not need many pesticides (to keep away bugs)[2] and no herbicides.[3] Linen and hemp were the most important fiber plants in Europe for a long time.
10,000 BCE
The origin of the plan is thought to be around nepal and northern china. > Learn more

2025 AD
Cultivation
Hemp is usually planted between March and May in the northern hemisphere, between September and November in the southern hemisphere.[87] It matures in about three to four months, depending on various conditions.
Millennia of selective breeding have resulted in varieties that display a wide range of traits; e.g. suited for particular environments/latitudes, producing different ratios and compositions of terpenoids and cannabinoids (CBD, THC, CBG, CBC, CBN...etc.), fiber quality, oil/seed yield, etc. Hemp grown for fiber is planted closely, resulting in tall, slender plants with long fibers.[88]
Water Use, Pesticide Use, Planting Schedule, Harvest time, Seeds, Testing, Equipment, Planning, Finnancing

Learn more about hemp Cultivation
Processing Manufacturing